Trending Now
Thursday, Nov, 2024
Home / Researchers From ISRO & IIT Guwahati detected polarised emissions from a black hole
Researchers From ISRO & IIT Guwahati detected polarised emissions from a black hole
The subject of scrutiny, Large Magellanic Cloud X-3 (LMC X3), is a binary star system housing a black hole and a 'normal' star significantly larger and hotter than our Sun. Positioned within a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, LMC X-3 resides approximately 200,000 light-years away from Earth.
 by Pragti Sharma /
by Pragti Sharma /  17 Nov 2023 21:51 PM IST /
17 Nov 2023 21:51 PM IST /  0 Comment(s) / 159
0 Comment(s) / 159

In an exceptional scientific achievement, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati (IIT Guwahati), partnered with the U R Rao Satellite Centre of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in Bengaluru. Their collaboration led to the groundbreaking discovery of polarized emissions from a black hole that exists beyond our Milky Way Galaxy. This monumental observation was made possible through advanced X-ray polarimetry techniques.
The subject of scrutiny, Large Magellanic Cloud X-3 (LMC X3), is a binary star system housing a black hole and a 'normal' star significantly larger and hotter than our Sun. Positioned within a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, LMC X-3 resides approximately 200,000 light-years away from Earth.
Despite decades of observation since its unearthing in 1971, comprehending the polarization traits of X-rays emitted by high-energy entities like stellar mass black holes remained a significant gap in astronomical understanding.
Professor Santabrata Das from IIT Guwahati emphasized the pivotal role of this breakthrough. "X-ray polarimetry serves as a unique beacon in identifying radiation sources near black holes. The emissions from LMC X-3, exceeding the Sun's potency by an astonishing 10,000 times, exhibit distinct polarization alterations upon interaction with the surrounding material enveloping these cosmic behemoths," elucidated Professor Das. These revelations offer profound insights into the gravitational interplay attracting matter towards black holes.
This extensive study, financially supported by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, India, has been published in the esteemed Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters. Spearheaded by Professor Santabrata Das and Dr. Anuj Nandi, the collaborative research team encompasses dedicated scholars—Mr. Seshadri Majumder from IIT Guwahati and Mr. Ankur Kushwaha from URSC, Bengaluru.

EShort / February 16, 2024
IMS Noida Admissions 2024: Apply for UG, PG programmes

EShort / February 16, 2024
GATE 2024: Response sheet out

EShort / February 16, 2024
BSSTET 2023: Admit card released

EShort / February 16, 2024
NID DAT 2024: Prelims result released

EShort / February 16, 2024
IIT JAM 2024: Response sheet released

Jobs / February 16, 2024
UPSC Recruitment Drive 2024: Apply for 120 vacancies in various departments

EShort / February 14, 2024
UPSC CSE 2024: Official Notification issued; application process begins

Editor's Desk / April 17, 2020
How Does Society Impact Our Education?

Current Affairs / April 22, 2020
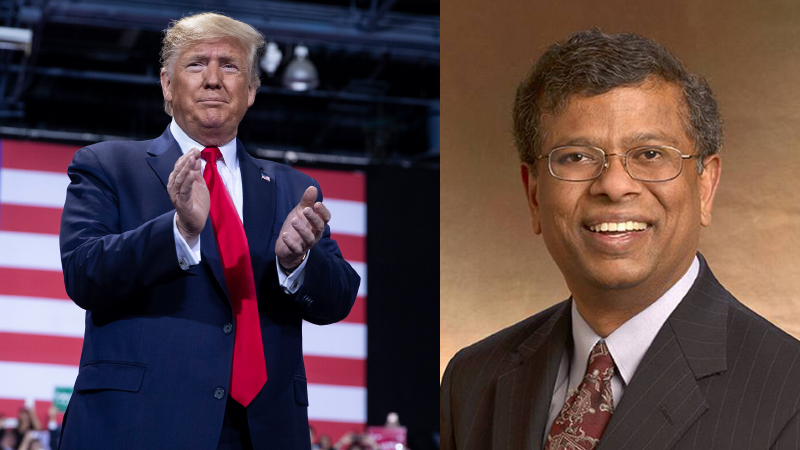
Mr. Sudarsanam Babu appointed to U.S. Science Board.

Reforms / April 17, 2020
Traditional Structure of Education In India
.jpg)
Events & Seminars / April 17, 2020
PISA!!

Blog / February 26, 2021
Government's Action On #ModiRojgaarDo

EShort / May 19, 2022
CUET PG 2025 has started the registration process.

Notice Board on Important Dates / April 21, 2020
World Heritage Day

News / July 08, 2021
JEE Mains Registration For Session 3: Last Date To Apply

EShort / December 14, 2021
UPSC Declared Final Result For DCIO Recruitment
























0 Comments
Post Comments