Trending Now
Thursday, Nov, 2024
Home / Researchers from IIT Madras Developed a Low-cost Approach to Mobile Pollution Monitoring
Researchers from IIT Madras Developed a Low-cost Approach to Mobile Pollution Monitoring
The IIT Madras researchers have developed a network capable of gathering spatiotemporal air quality data by equipping vehicles with low-cost air quality sensors. The Indian Institute of Technology Madras stated that this seeks to allow the mapping of an entire city at high resolution at the cost of a single reference monitoring station.
 by Pragti Sharma /
by Pragti Sharma /  16 Jun 2023 21:49 PM IST /
16 Jun 2023 21:49 PM IST /  0 Comment(s) / 256
0 Comment(s) / 256
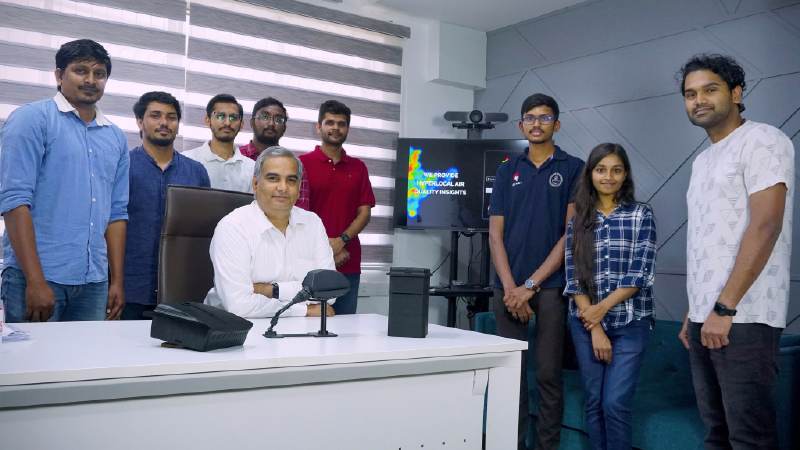

Image Courtesy : www.facebook.com/ReachIITM
The Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (IIT Madras) researchers have developed data science and IoT-based practice for mobile pollution monitoring. This framework developed by the researchers permits pollution sensors scaled on public vehicles to monitor the air quality of an extended area at an increased spatial and temporal resolution.
The IIT Madras researchers have developed a network capable of gathering spatiotemporal air quality data by equipping vehicles with low-cost air quality sensors. The Indian Institute of Technology Madras stated that this seeks to allow the mapping of an entire city at high resolution at the cost of a single reference monitoring station.
The project titled Kaatru, meaning air in Tamil, seeks to acquire a pan-India hyper-local air quality map, perform exposure assessments for Indian citizens, and develop data-driven resolutions for policy, intervention, and mitigation techniques.
The paper describes the data science and IoT-based mobile monitoring framework for achieving high-resolution spatiotemporal assessments and effective spikes in PM2.5 pollution during specific times, such as when trucks carrying milk pass via particular areas and during school opening and ending hours.
The affordability and efficacy of the IoT-based mobile monitoring network, integrated with data science principles, deliver exceptional benefits in collecting hyperlocal understandings of air quality, allowing informed mitigation and policy decisions.
The IoT mobile monitoring devices can measure numerous parameters, including PM1, PM2.5, and PM10, as well as gases like NOx and SOx. The devices can consider road roughness, potholes, and UV index, among other elements. The patented IoT side view mirror design facilitates the developed devices to be retrofitted on diverse vehicles, from buses to cars and even two-wheelers.
In order to validate the dependability of the data gathered by the IoT, the researchers performed two case studies. The first case study concentrated on hyperlocal air quality assessments in a carefully chosen area in western Chennai. The case study caught slight variations in PM2.5 concentrations across various locations and roads, delivering beneficial insights into pollution patterns.
The second study examined PM2.5 levels during the high-intensity event of Deepavali. The data accumulated from the IoT devices corresponded to that of a Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) station, and a high qualitative match was followed, validating the dependability of the mobile monitoring system.

EShort / February 16, 2024
IMS Noida Admissions 2024: Apply for UG, PG programmes

EShort / February 16, 2024
GATE 2024: Response sheet out

EShort / February 16, 2024
BSSTET 2023: Admit card released

EShort / February 16, 2024
NID DAT 2024: Prelims result released

EShort / February 16, 2024
IIT JAM 2024: Response sheet released

Jobs / February 16, 2024
UPSC Recruitment Drive 2024: Apply for 120 vacancies in various departments

EShort / February 14, 2024
UPSC CSE 2024: Official Notification issued; application process begins

Editor's Desk / April 17, 2020
How Does Society Impact Our Education?

Current Affairs / April 22, 2020
Mr. Sudarsanam Babu appointed to U.S. Science Board.

Reforms / April 17, 2020
Traditional Structure of Education In India
.jpg)
Events & Seminars / April 17, 2020
PISA!!

Blog / February 26, 2021
Government's Action On #ModiRojgaarDo

EShort / May 19, 2022
CUET PG 2025 has started the registration process.

Notice Board on Important Dates / April 21, 2020
World Heritage Day

News / July 08, 2021
JEE Mains Registration For Session 3: Last Date To Apply

EShort / December 14, 2021
UPSC Declared Final Result For DCIO Recruitment
























0 Comments
Post Comments